Organizations are increasingly reliant on cloud-based services to enhance productivity and collaboration. Microsoft 365, with its suite of services like SharePoint, ExchangeOnline, OneDrive and Teams, has become a cornerstone for many businesses. However, with the advantages of cloud computing come heightened security risks, making it essential to implement robust security frameworks. In this article we will explain how M365 CIS Benchmark and Microsoft Zero Trust Security Model are tightly integrated to provide robust security for your cloud environment.
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) has developed benchmarks that provide a comprehensive set of best practices for securing various technologies, including Microsoft 365. These benchmarks are particularly relevant in the context of the Zero Trust security model, which advocates for a “never trust, always verify” approach to cybersecurity. This article delves into how the CIS Benchmark for Microsoft 365 supports the implementation of the Zero Trust model, providing organizations with a structured approach to enhancing security in their cloud environments.
The CIS Benchmark for Microsoft 365 is a set of guidelines designed to help organizations secure their Microsoft 365 environments effectively. The benchmarks include recommendations for configurations, settings, and policies across various components of Microsoft 365, such as Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Microsoft Teams.
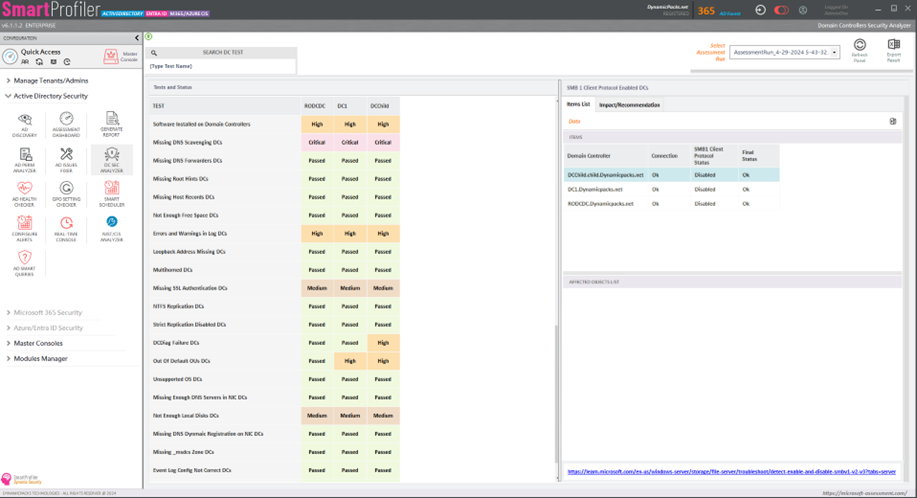
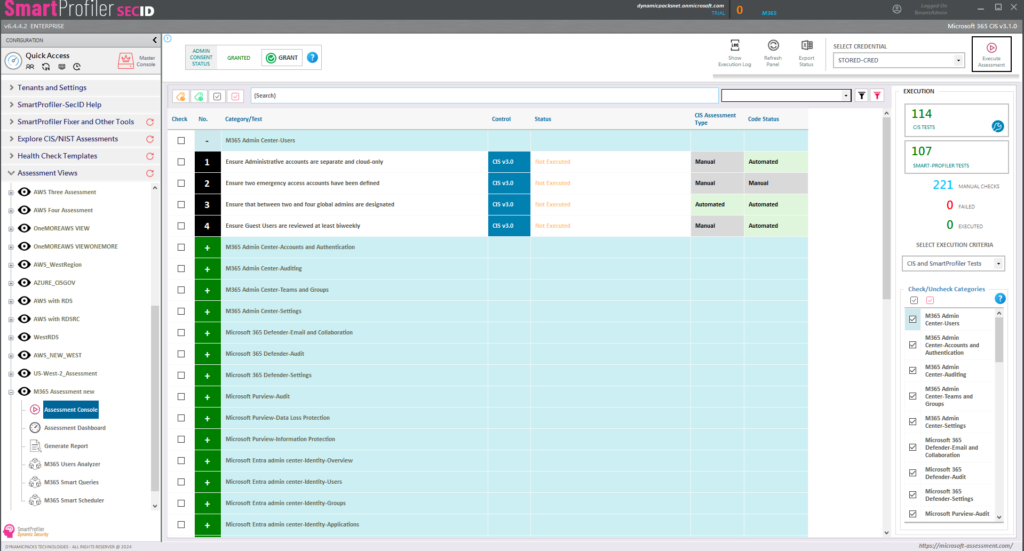
SmartProfiler-SecID, an improved version of SmartProfiler, now supports doing M365 CIS Assessment for latest controls implemented by the CIS organization.
M365 CIS Benchmark and Microsoft Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust security model represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. Traditional security models often relied on a perimeter-based approach, assuming that users and devices within the network were trustworthy. However, this approach has become increasingly ineffective in the face of sophisticated cyber threats.
Key Principles of Zero Trust
The CIS Benchmark for Microsoft 365 aligns closely with the principles of the Zero Trust security model. By implementing the recommendations outlined in the benchmark, organizations can effectively enhance their security posture and support Zero Trust principles.
1. User Identity and Access Management
One of the fundamental tenets of Zero Trust is the verification of user identities. The CIS Benchmark emphasizes strong identity and access management practices, which are essential for implementing Zero Trust.
Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
The benchmark recommends implementing MFA for all users. MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors, such as a password and a temporary code sent to their mobile device. This additional layer of security makes it significantly more challenging for unauthorized users to gain access, even if they have stolen credentials.
Conditional Access Policies
Conditional access policies allow organizations to set specific conditions under which users can access resources. For example, access might be restricted based on the user’s location, device compliance, or risk level. By leveraging these policies, organizations can ensure that only trusted users can access sensitive resources.
2. Data Protection and Encryption
Data security is a critical aspect of the Zero Trust model, and the CIS Benchmark provides comprehensive guidelines for protecting sensitive data.
Data Classification
Organizations should classify their data based on sensitivity levels. The CIS Benchmark encourages the use of data classification schemes to identify and protect sensitive information, ensuring that appropriate security controls are applied.
Encryption
The benchmark emphasizes the use of encryption for data at rest and in transit. Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized users, it remains unreadable. This aligns with Zero Trust principles by protecting data irrespective of its location.
3. Threat Detection and Response
Continuous monitoring and logging are essential for maintaining a Zero Trust environment. The CIS Benchmark encourages organizations to enable logging features across Microsoft 365 services, allowing for real-time threat detection and incident response.
Enabling Audit Logs
Organizations should enable audit logs to track user activities and changes within Microsoft 365 applications. These logs provide valuable insights into user behavior and can help identify suspicious activities.
Integrating Microsoft 365 logs with a SIEM solution enables organizations to analyze data from multiple sources in real time. This enhances threat detection capabilities and allows for quicker responses to potential security incidents.
4. Configuration Management
Configuration management is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. The CIS Benchmark outlines best practices for securing configurations across Microsoft 365 applications, helping organizations ensure that their settings align with Zero Trust principles.
Regular Configuration Reviews
Organizations should conduct regular reviews of their Microsoft 365 configurations to identify any deviations from best practices. This proactive approach helps maintain security and compliance.
Automated Configuration Monitoring
Implementing automated tools for configuration monitoring can help organizations quickly identify and remediate configuration drift. These tools can alert administrators to unauthorized changes, enabling rapid response to potential security threats.
5. User Training and Awareness
User behavior plays a crucial role in maintaining security. The CIS Benchmark recommends implementing user training and awareness programs to educate employees about security best practices.
Security Awareness Training
Regular security awareness training helps employees recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other common threats. Informed users are less likely to engage in risky behaviors that could compromise security.
Simulated Phishing Exercises
Conducting simulated phishing exercises can test employees’ awareness and response to phishing attempts. These exercises provide valuable insights into areas where additional training may be needed.
Implementing the CIS Benchmark for Microsoft 365
Step 1: Assess Current Security Posture
Organizations should begin by assessing their current security posture in relation to the CIS Benchmark. This involves conducting a thorough audit of existing configurations, policies, and practices within Microsoft 365.
Step 2: Prioritize Recommendations
After assessing the current state, organizations should prioritize the recommendations outlined in the CIS Benchmark based on their risk profile and business objectives. Focus on areas that present the highest security risks and require immediate attention.
Step 3: Develop an Action Plan
Create a detailed action plan that outlines the steps needed to implement the recommended security controls. This plan should include timelines, responsibilities, and resource requirements.
Step 4: Implement Controls
Begin implementing the recommended controls in accordance with the action plan. This may involve configuring settings, enabling features, and conducting user training.
Step 5: Monitor and Review
Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the implemented controls and review their alignment with the CIS Benchmark. Conduct periodic audits to identify areas for improvement and ensure that security practices evolve in response to emerging threats.
The CIS Benchmark for Microsoft 365 provides organizations with a comprehensive framework to enhance their security posture while supporting the principles of the Zero Trust security model. By implementing the recommendations outlined in the benchmark, organizations can effectively protect their Microsoft 365 environments against evolving cyber threats.
In an era where remote work and cloud services have become the norm, adopting a Zero Trust approach—bolstered by the CIS Benchmark—will be crucial for organizations seeking to safeguard their sensitive data and maintain trust with their stakeholders. The integration of these practices not only strengthens security but also fosters a culture of security awareness among employees, ensuring that organizations are better prepared to navigate the complexities of the modern cybersecurity landscape.
Please check articles from Vendors
Try SmartProfiler, a unified tool to help with security evaluation across many Microsoft technologies.