Active Directory (AD) is a critical component of enterprise IT environments. It serves as a central repository of information about network resources, user accounts, and access rights. As such, it plays a vital role in network authentication and authorization. However, as cyber threats continue to evolve, it is important to assess the security of Active Directory regularly. This article will explore the common security risks associated with AD and the importance of conducting a comprehensive Active Directory Security Assessment for an Active Directory environment. Article explains why Active Directory security assessment is needed.
An advanced Active Directory security assessment involves evaluating various aspects of the AD environment to identify potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and security risks. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct such an assessment:
Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft. It provides a central location for managing network resources, such as computers, users, and printers. The AD infrastructure consists of domains, domain controllers, and various other objects, including users, groups, and organizational units (OUs).
Securing Active Directory is critical to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information. If AD is compromised, attackers can gain access to sensitive data, escalate privileges, and execute various types of attacks. As such, it is important to understand the potential security threats to Active Directory.
A. Password Weaknesses- Weak passwords are one of the most common security risks in AD environments. Users often use predictable or easily guessable passwords, such as “password123” or “123456.” Attackers can use password cracking techniques to gain access to user accounts and then escalate privileges to gain access to sensitive information.
B. Privilege Escalation- Privilege escalation occurs when an attacker gains elevated access to a system or resource. In an AD environment, an attacker may exploit a vulnerability to escalate privileges to gain access to sensitive data or resources.
C. Unauthorized Access- Unauthorized access occurs when an attacker gains access to an AD resource without proper authorization. Attackers can gain access through various means, such as exploiting vulnerabilities, using stolen credentials, or taking advantage of configuration weaknesses.
D. Malware and Ransomware Attacks- Malware and ransomware attacks are becoming more common in AD environments. Attackers can use malware or ransomware to compromise an AD environment, encrypt sensitive data, and demand ransom payment. The impact of such attacks can be severe, including data loss, system downtime, and reputational damage.
Conducting a comprehensive AD security assessment can help organizations identify vulnerabilities and implement proactive risk mitigation strategies.
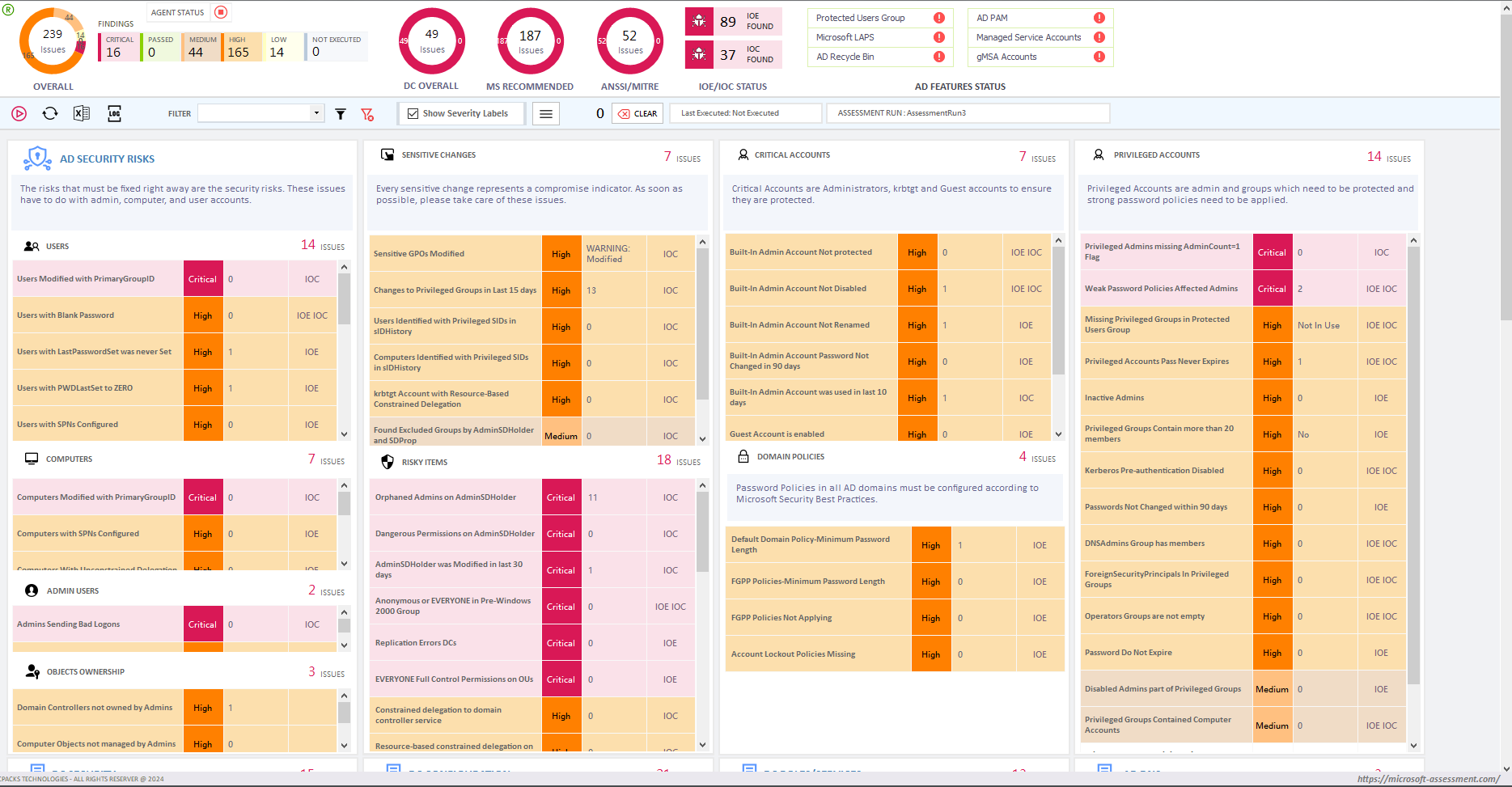
A. Identifying Vulnerabilities- Identifying vulnerabilities is critical to securing an AD environment. An AD security assessment can help identify security weaknesses in the AD infrastructure, such as weak passwords, misconfigured group policies, and unsecured privileged accounts.
B. Proactive Risk Mitigation-Proactive risk mitigation strategies help prevent security incidents before they occur. An AD security assessment can help identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited, reducing the risk of a data breach or cyberattack.
C. Compliance Requirements- Many industries have compliance requirements that organizations must meet to avoid legal or financial penalties. An AD security assessment can help organizations meet compliance requirements, such as those specified in HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR.
To conduct a comprehensive AD security assessment, there are several key components that should be considered. These components help to ensure that all aspects of the AD environment are thoroughly evaluated, and potential security vulnerabilities are identified and addressed.
A. User Account Review- The first component of an AD security assessment is a user account review. This involves analyzing user accounts to ensure that they are valid, active, and properly configured. User accounts should be reviewed to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive resources and that permissions are properly configured.
Additionally, dormant or unauthorized accounts should be identified and addressed, as these accounts can pose a significant security risk. By conducting a user account review, organizations can ensure that their AD environment is properly configured and secure.
B. Group Policy Analysis- The second component of an AD security assessment is a group policy analysis. Group policies are used to configure security settings for groups of users or computers. These policies can be used to enforce password policies, restrict access to certain resources, and control user settings.
By analyzing group policy settings, organizations can ensure that their AD environment is properly configured and that security policies are being enforced. Additionally, organizations can identify any misconfigurations or vulnerabilities in their group policy settings and take corrective action.
C. Audit Log Analysis- The third component of an AD security assessment is an audit log analysis. AD generates audit logs that record events such as logins, resource access, and changes to the AD environment. By analyzing these audit logs, organizations can identify potential security threats and take corrective action.
Audit log analysis can also be used to detect unauthorized access attempts, account misuse, and other security violations. By implementing audit log analysis tools and techniques, organizations can ensure that their AD environment is secure and compliant with industry standards and regulations.
D. External Vulnerability Scanning- The fourth component of an AD security assessment is external vulnerability scanning. External vulnerability scanning involves testing the AD environment from an external perspective to identify potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
By conducting external vulnerability scanning, organizations can identify potential security weaknesses in their AD environment and take corrective action. External vulnerability scanning can also be used to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOX.
Performing an AD security assessment involves a series of steps that need to be followed systematically. The following section provides a step-by-step guide to conducting an AD security assessment.
A. Scoping the Assessment-The first step in conducting an AD security assessment is to define the scope of the assessment. Scoping helps to establish the objectives of the assessment and determine the areas that need to be assessed. Factors to consider when defining the assessment scope include the size of the AD environment, the complexity of the infrastructure, and the criticality of the AD resources.
B. Gathering Information-The next step is to collect relevant information about the AD environment. This involves gathering data about the AD infrastructure, user accounts, access rights, and security configurations. Various tools and techniques can be used for data gathering, including network scanners, AD query tools, and audit log analysis tools.
C. Analyzing the Collected Data-Once the data has been collected, the next step is to analyze it. The analysis process involves identifying vulnerabilities, assessing risk levels, and determining the impact of potential threats. Different assessment methodologies and frameworks can be used to guide the analysis process.
D. Reporting and Recommendations- The final step is to document the assessment findings and provide actionable recommendations. A clear and concise report should be prepared to communicate the assessment results and recommendations to stakeholders. The report should include an executive summary, a detailed analysis of the assessment findings, and recommendations for addressing identified vulnerabilities and risks.
Conducting an AD security assessment is not a one-time event. To maintain a secure AD environment, continuous monitoring and maintenance are essential. Ongoing monitoring helps to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time, while maintenance helps to ensure that security configurations and policies remain up-to-date.
Looking to assess the health and security of your Active Directory environment? Microsoft-Assessment.com offers free Active Directory Security Assessment and AD Health and Security Assessment services. With SmartProfiler Active Directory, we diagnose and resolve issues like replication problems, DNS misconfigurations, and database corruption. Our expert team also evaluates your AD security posture and helps you implement best practices. Experience active monitoring, auditing, and protection for your AD environment. Visit Microsoft-Assessment.com today for a comprehensive AD assessment. SmartProfiler for Active Directory performs advanced assessment and follow all security practices recommended by ANSSI, MITRE and Microsoft.
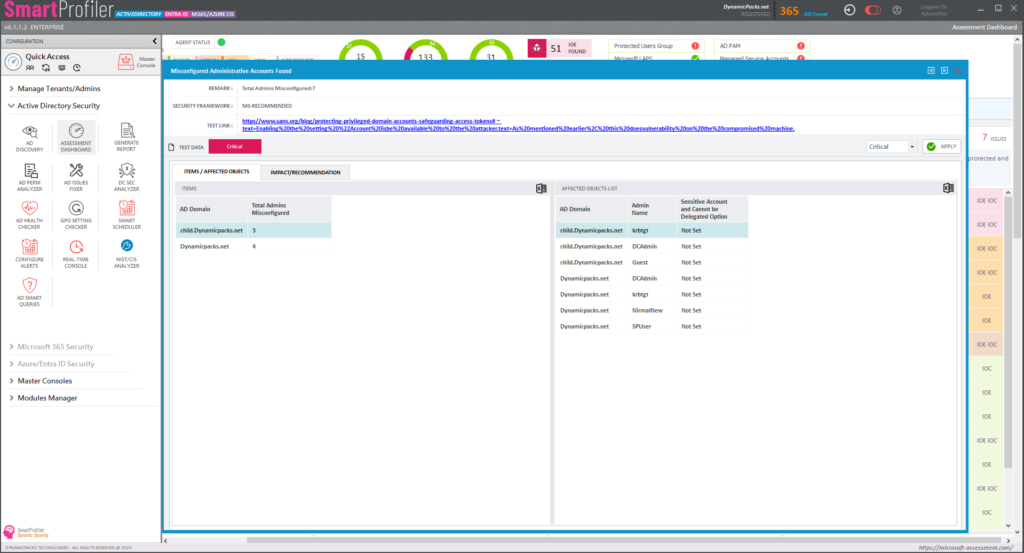
Try SmartProfiler, a unified tool to help with security evaluation across many Microsoft technologies.